Why is technical SEO important for eCommerce?
Imagine you have a beautiful, designed house. You might have a perfectly decorated façade and astonishing interior design but, if its foundation isn’t well structured and solid enough, the house itself could crumble away easily. The same goes for your eCommerce website, no matter how great your content is, there might be technical aspects that keep your site from performing at its best.
With the rise in eCommerce websites in the last few years, it is even more important to ensure you have a well-performing website which delivers both a great user and crawler experience.
But first, what is technical SEO?
SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) generally focuses on maintaining and improving the overall organic visibility of a website on Search Engines. Technical SEO is one of its subcategories, including all the technical aspects that ensure Search Engines and bots can access and understand your website as easily and efficiently as possible.
Technical SEO audits can be daunting, and you might wonder where to start. Luckily, we designed an ultimate technical SEO checklist to guide you through the basic checks and fixes required.
Table of Content
Technical Audit
Crawlability and Indexability
Broken Links
When a resource cannot be found, the page will return a 404 HTTP error and it results in a broken link. If search engines encounter too many broken links, this may negatively impact the performance. Nevertheless, this provides a poor user experience and fails to reallocate link equity. This issue applies to all kinds of websites but imagine a user looking for a product on your eCommerce site and landing on a 404 page, that could disrupt the whole user journey and potentially result in revenue loss.
To avoid that, simply review all the broken links in your site and redirect to relative pages with a 200-status code and indexable. The ScreamingFrog tool is a good starting point to check broken links present on your site.
XML Sitemaps
XML sitemaps provide search engines with a list of webpages that needs to be crawled. It basically tells Search Engines what pages are the most important on your site. Therefore, it is important that the XML sitemap lists every live landing page with the correct XML protocol. All pages should be the self-referencing canonical and return a 200-status response code. This is particularly vital for an eCommerce site as they usually have many product pages therefore if the correct pages aren’t included in the XML sitemap it could negatively affect the crawlability and indexability of important pages.
Explore our XML Sitemap Generator to help you create an XML sitemap and submit it to Search Engines.
HTML Sitemaps
The HTML Sitemap is a Google accessibility best practice. In a few words, it is an HTML page that lists all the main live landing pages to improve both search engines and users’ experience. Ecommerce sites continuously expand, adding new products or category pages, so it can get confusing for users to understand what’s on your site. Keeping an updated HTML sitemap offers an overview of all the important pages on your eCommerce site and facilitates users’ navigation.
Robots.txt
The Robots.txt file allows a webmaster to control what content a given search engine visits and indexes. This can be a powerful tool for eCommerce websites, and it is vital that important pages are not blocked from crawling or indexing, while less valuable pages are not wasting crawl budgets. If you are experiencing issues with some of your pages, we advise exploring our robots.txt checker tool to validate and test your robots.txt file.
Orphan Pages
Ecommerce sites will often create new pages therefore, it is vital to plan internal linking accordingly to avoid issues with Orphan pages. But what are exactly Orphan pages? Simply, they are pages that have no internal links pointing to them, isolated from the rest of the pages on your site. The result will be a lack of indexation for those pages as search engines cannot find them.
We advise to review the Orphan pages present on your site, if any, and link to other relevant pages on your site. Check out the ScreamingFrog guide on how to find Orphan Pages.
Navigation and Site Structure
Faceted Navigation
Faceted navigation is often used in eCommerce as it simplifies site search for users. Nonetheless, faceted navigation can cause issues for SEO as they generate a new URL for every filtered search, usually by adding parameters and possibly resulting in duplicate content. It is important to follow best practices to avoid common issues:
- Remove empty values on parameters
- Keep the same parameters order across all URLs
- Block parameter URLs via robots.txt file to prevent crawling
- Canonicalised parameter URLs
- Use Nofollow attribute for any internal link to filtered pages
Canonical Tags
Canonical tags are used to prevent duplication issues across pages on your website. Often, eCommerce sites have similar content across several pages, think about the category or product pages; these pages can be seen as duplicate content by Search Engines and have a negative impact on the ranking and indexability of your pages. Practically, canonical tags tell Search Engines which page should be considered as the official one. Here are some best practices to use canonical tags correctly:
- Canonical pages must have a 200-status code and be Indexable
- Self-referential Canonical tags
- Every page should have one canonical tag, use a self-referential tag for the canonical page.
- Review dynamic canonical tags
- Cross-domain canonicalization
Internal Linking
Internal links are very important as they can help Search Engines understand and rank better your website; additionally, internal links support users to navigate related pages across your website. Having an internal linking strategy supports the overall site structure and helps avoid issues with Orphan pages. Ultimately, great internal linking will help deliver a great user experience and engagement which is even more important for eCommerce sites as it can boost the overall retention and revenue.
One last note, when building internal links, it is important to optimise Anchor text for SEO. To best optimise your Anchor text, it should be:
- Concise and Descriptive
- Keep the link text as concise as possible
- Relevant to the linked page
- The link text needs to refer to the topic of the source page
- Right keyword density
- Don’t overdo with keywords, use only the right amount of relevant keywords
Pagination
The term pagination refers to how your website deals with content which does not fit entirely onto users’ screens. As you can imagine, this often occurs on eCommerce sites, just think about a long product list on one category page. As easy as it could seem to implement pagination solutions, it needs to be done correctly to have the best positive impact on the authority and visibility of paginated pages. Ultimately, what’s most important is offering the best user experience possible nonetheless, there are important considerations to keep in mind:
- Canonical Tags
- Use self-referencing for each paginated page
- Do not use no-index tags
- Internal Linking
- Include link relevant links between paginated pages, particularly for pages that can only be found through pagination
- Add pages located deep in the site to your sitemaps, this supports Google finding them
- JavaScript
- Google cannot follow any link that’s triggered from an event, so be sure to include links to paginated pages by using the <a> tag with an href attribute.
URL Structure
ECommerce sites usually have several products which results in the creation of several URLs. It is important to keep their structure as clear and consistent as possible across your site to support user-friendliness and boost click-through-rate. Let’s have a look at 5 URL structure best practices:
- Keep URLs short, simple and logical
- Only use hyphens to separate multiple words
- Use relevant words to the page
- Always use lower case letters
- Ensure consistency
Additionally, it is important to optimise parameters to avoid duplication issues, as previously discussed in the Faceted Navigation section above.
Performance Enhancement
Site Speed
Core Web Vitals
In May 2020 Google introduced the Core Web Vitals (CWV) to measure the quality of user experience and they focus on three aspects: loading, interactivity and visual stability. CWV are measured by: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), respectively. You can easily check your website CVW on Google Search Console to identify if or which URLs are failing the CWV for any of the above metrics. Below there are a few actions you can take to improve your CWV:
- LCP
- Remove unused third-party scripts
- Lazy load assets below the fold
- Remove large elements
- Minify CSS
- FID
- Minimize or defer JavaScript
- Remove non-critical third-party scripts
- Use a browser cache
- CLS
- Use size attribute to set dimensions for media
- Reserve specific spaces for Ads
- Add new UI elements below the fold
Mobile Optimisation
In the past few years, the mobile traffic for eCommerce sites has seen consistent growth, but there are still many challenges eCommerce sites are facing when it comes to mobile optimisation.
There are three main considerations to make your site mobile-friendly:
- Think mobile users: ensure effectiveness by prioritising tasks, ensuring users can easily complete their goals and keeping a consistent interface across platforms.
- Use responsive web design: keeping the same URL for all devices and ensuring the pages adjust to different screen sizes.
- Optimise site speed: delivering a fast experience does make the difference for users nowadays. Refer to our Core Web Vitals guidelines above to offer the best experience in your eCommerce.
These considerations will help deliver a better user experience, increasing both retention and conversion. Learn if the pages on your website are optimised for mobile by using our Mobile-Friendly Test. Additionally, you can explore if your site is ready for Google’s mobile-first index with our Mobile-First Index Tool.
Additionally, it is worth including one additional consideration for mobile eCommerce regarding the use of Interstitial Ads. These Ads are widely used as they can result in positive returns. Back in 2017, Google introduced a penalty for interstitials to reduce the use of intrusive interstitials and further support a better user experience. Ensure you don’t get affected by this penalty by following three mobile best practices when designing popups:
- Popup should take up no more than 25% of the viewport:
- Full-screen interstitial allowed only for cookies or age-verification purposes.
- Popup should be easily dismissible by the user:
- Always include an easy way to get out of a popup.
- Popup should not be shown before user interaction or during critical tasks:
- Don’t show popups immediately after the user navigates to a page from the search results.
- Don’t show popups while they are looking through the page.
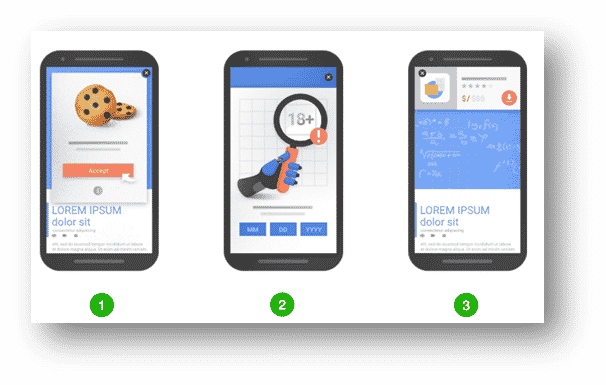
3. Ads popup (25% of the screen)
Image and Video Optimisations
Most websites include images and videos, but these files aren’t always optimised. Below there’s a list of key optimisations to support user experience, accessibility and the overall website performance:
- Images
- Contain descriptive alt texts
- Use Next-Gen formats such as WebP and JPG2000
- Are compressed and resized to scale
- Heights and widths are defined
- Videos
- Are available on a public, indexable page
- Are wrapped within an appropriate HTML tag
- Schema markup is added
Both images and videos are included in the XML sitemap or if your websites contain many videos and images, create a separate XML site map for them.
Internal Redirects
Internal redirects send both users and bots to a different URL from the one originally requested to another one within the same website. Too many internal redirects can strain the server, resulting in slower page speeds. Often, redirect loops may be indicative of poorly handled migrations. As best practice, all internal links should always lead to a page with a 200-series HTTP response.
Structured Data
By providing more semantic context to the site’s content, structured data (aka Schema) can enhance the search experience, improve organic Click-Through-Rate, and positively improve ROI. While using structured data is important for every website, it is even more essential for eCommerce sites as they are usually considerably larger and have various content across different page types. Implementing structured data correctly across your site can be confusing, but it is fundamental to get the best results. If you’re struggling, check out our Schema Markup Generator (JSON-LD) to help you create schema markups correctly. Also, don’t forget to validate your structured data code before implementing it, you can easily do that by using the Schema.org testing tool.
Schema Best Practices
- Implementing Schema will help search engines to understand your content and help create rich snippets to be displayed in search results.
- Adding Schema to apps provide search engines with additional information about an app, including its specifications, rating, and price. This aesthetically enhances the look of the search result of the app within returned search results (especially mobile search listings), ultimately resulting in more clicks and potentially more downloads and installs.
- Schema for breadcrumbs helps search engines to understand the structure of the website. Breadcrumbs also help users orient themselves on a site.
- Google strives to understand the relationships between different entities on the internet as well as facts about people, things, and places. It is important for brand presence to have some appearance within Google Knowledge Graph for brand queries.
6 Common Mistakes
- Marking up content that is invisible to users:
- Star Reviews, for example, are often listed on the bottom of the page or an additional click away from the core landing page. In these instances, we see sites using schema markup to add context and text to the page without being user-visible text.
- Applying a page-specific markup sitewide:
- This practice can also be seen as manipulative and lead to a penalty. To avoid manual action, use the markup for a specific product, not a category or a list of products.
- If using schema markup on a series of products, Google recommends ensuring that you are only listing the top-level topic and aggregating/or averaging the reviews and ratings.
- Structured data manipulation:
- Marking up reviews that were written by the company, not real customers.
- Using individual ratings as opposed to average ratings.
- Delivering different structured data based on user detection:
- Amending the page’s content based on user detection, particularly with international sites, is a tempting solution. But, doing so can be perceived as a manipulative action. The ideal scenario is that the markup remains the same across sites and in different locations.
- Sites using AngularJS or Ajax to populate on-site content:
- Sites that are using AngularJS need to ensure that schema markup is added into the header, passed through the DOM or utilises third-party script to ensure the code can be rendered on the page.
- Using similar tags on the page in relation to the same element:
- Many schema.org tags seem similar at first, but it is fundamental to apply the correct ta to the correct elements to get effective results.
Results-Driven Actions
Case Studies
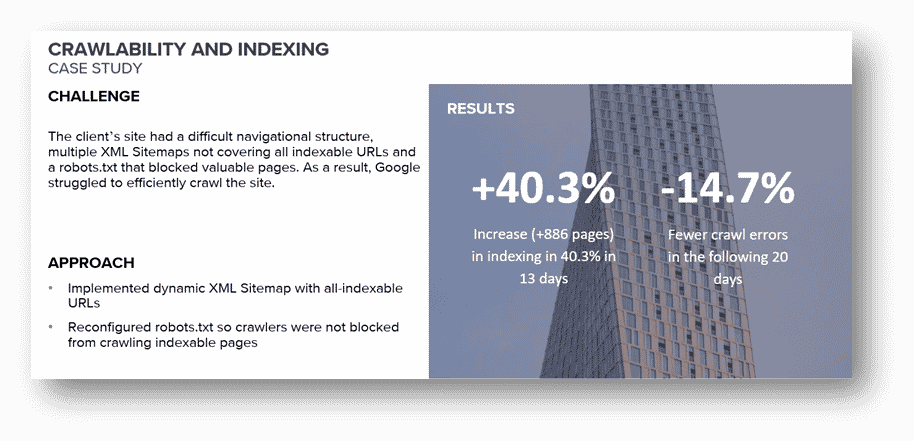
Crawlability and Indexing Case Study
The client’s site had a difficult navigational structure and its XML Sitemap and Robots.txt weren’t optimised. By implementing technical fixes Client’s site indexability increased by 40.3% (886 pages) in just 13 days, and crawl errors were reduced by -14.7% in the following 20 days.
Internal Linking Case Study
The client’s site, NetAnAgent, had several key pages nestled deep in the site structure which were given less merit by Search Engines. Merkle implemented breadcrumbs and an HTML Sitemap to improve the internal linking structure. The results were a growth of +104% in keywords ranking, +707 key terms ranking +50 positions higher and a positive increase in keywords ranking on pages 1 to 3.
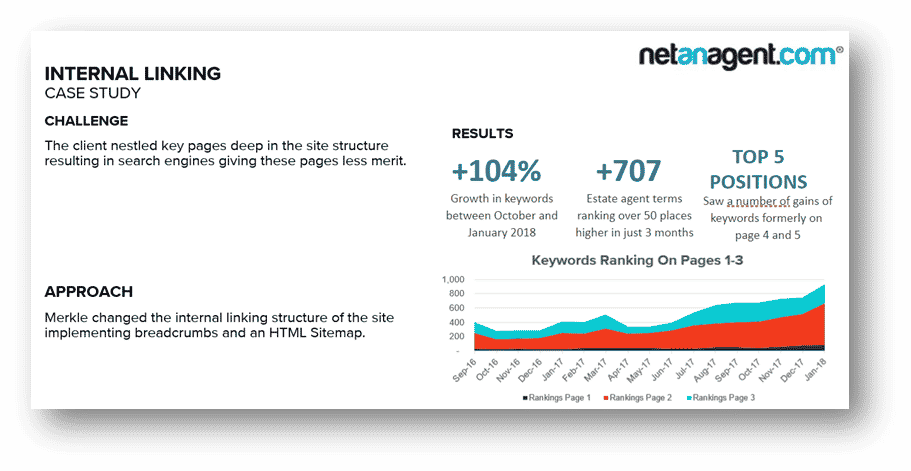
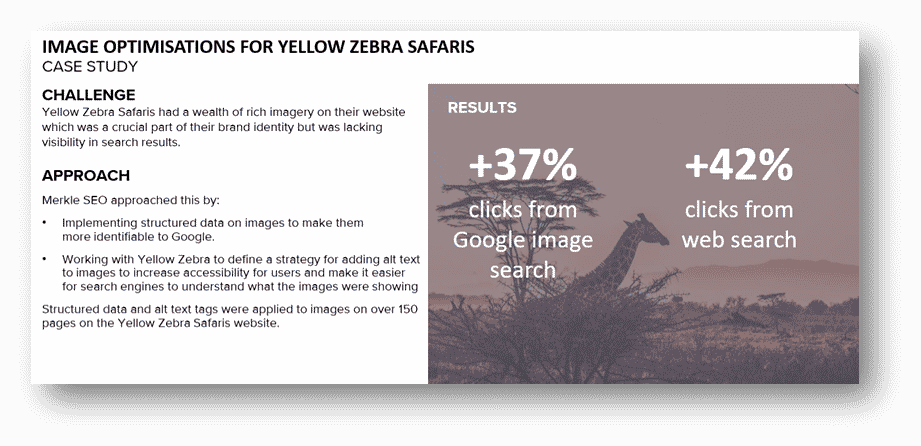
Image Optimisations Case Study
Yellow Zebra Safaris’s site had a wealth of rich imagery which was crucial to their brand identity. Merkle identified an opportunity to optimise the images’ visibility. By implementing structured data and optimised Alt text over 150 pages which led to +37% clicks from Google image search and +42% clicks from web search.
Prepare your eCommerce Site For Peak Season
By tackling some of the most common SEO challenges for eCommerce websites, this checklist will enable you to build a great technical foundation for your website. This is the time to prepare your site to be as optimised and user-focused as possible, so to thrive during peak season.